Previous lesson, division of attention.
Introduce 8’s on Pylons maneuver. Allow the student to explain and perform the maneuver. Purpose: subconscious control of the airplane. Fly at a constant bank angle, varying altitude so the line parallel to the airplane’s lateral axis, extending from the pilot’s eye, appears to pivot on each of the pylons. Distance from pylon may vary with wind.
Phil the photographer needs some perfect pictures of an airplane wing appearing to rest beneath a silo on the ground. He spent most his money on a new camera, and has hired you to help him get the photograph. Can you help? Phil calculated that he can only pay you for your time and 15 minutes at the selected silo.
Read AFH & watch video
AFH 6-12; Area of Operation V, Task E
Definitions:
- Pivotal altitude: A specific altitude at which, when an airplane turns at a given groundspeed, the airplane appears to pivot around a single ground reference point.
- Pylon: easily distinguishable object on the ground
Preflight Briefing: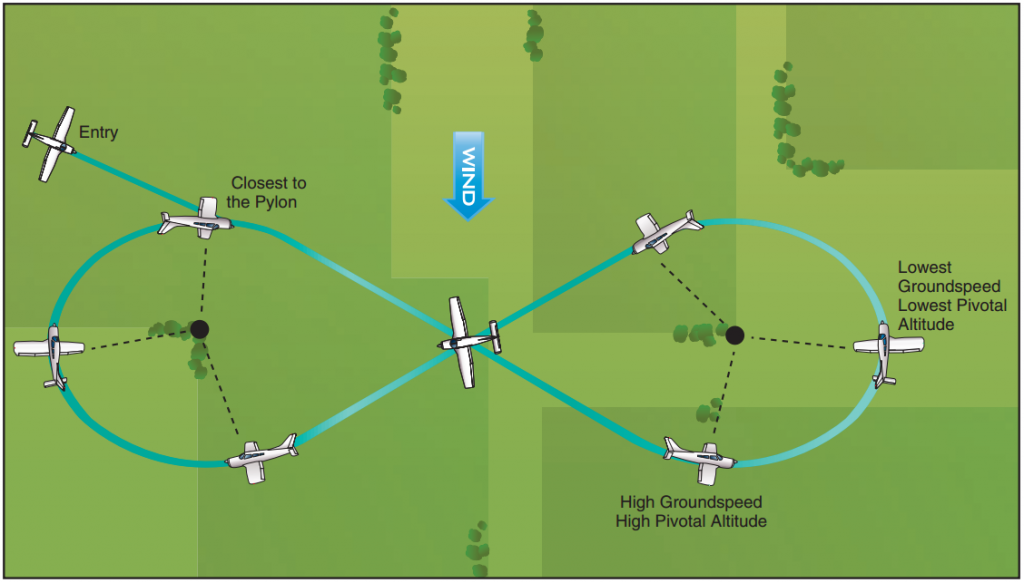
Common errors:
- Failure to adequately clear the area.
- Skidding or slipping in turns (whether trying to hold the pylon with rudder or not).
- Excessive gain or loss of altitude.
- Over concentration on the pylon and failure to observe traffic.
- Poor choice of pylons.
- Not entering the pylon turns into the wind.
- Failure to assume a heading when flying between pylons that will compensate sufficiently for drift.
- Failure to time the bank so that the turn entry is completed with the pylon in position.
- Abrupt control usage.
- Inability to select pivotal altitude.
Special Emphasis Areas:
- Maintain coordinated flight at all times.
- Divide attention between instruments and outside the aircraft.
Completion Standards:
See Airman Certification Standards
Flight phrasology:
(To Regain pivotal altitude)
- Dive forward to the pylon
- Climb back to the pylon
Post-Flight Debriefing:
Identify tasks that were completed to standards or above.
Identify and discuss tasks that were not completed to standards.
Record and grade completed tasks in the training record.
Record training in the student’s logbook (reference Areas of Operation above)
Give an assignment for the next flight session.
Next Assignment: Prepare for completing this lesson by reviewing tasks that were not performed to standards. If all tasks were performed to standards, assign the next lesson’s required material.