Arranged by Certificate and Rating
Many of these memory items will apply to multiple areas of your flying, but are categorized by when they are generally first learned.
See the Full List Below
IFR Equipment Required
Lost engine memorized checklist
Risk Elements PAVE
Decide Model
VFR Visibility/Cloud Clearance
Special Use Airspace
Lost 5 C’s VFR Cross Country
Night Definition
Hazardous Attitudes
Multi-Engine Aerodynamics
Fundamentals of Instruction
Instructor Endorsements
DIE
Documents for Airworthiness
ARROW
Airworthiness certificate 91.203(a)(1)
Registration (temporary is pink) 91.203(a)(2)
Radio license (international flights & IFR) 91.711(c) 91.205(d)(2)
Operation handbook 91.9
Weight & balance 91.103(b)(2)
Inspections for Airworthiness
91.409, 91.207, 91.411, 91.413. 91.417
AVIATES
Annual (12 months)
VOR Check (30 Days)
100 Hour or Progressive inspection
(required if aircraft is used for hire or flight instruction for hire—91.409(b))
Altimeter (24months 91.411) and
Airworthiness Directives
Transponder (24 months 91.413)
ELT (12 months)
Static inspection (24 months)
Equipment for Airworthiness
Required for VFR flight 91.205(b)
ATOMS 2 FLEA
Airspeed indicator
Altimeter
Tachometer (for each engine)
Temperature (each liquid cooled engine)
Oil pressure gauge (each engine using pressure system)
Oil temperature gauge (each air cooled engine)
Magnetic direction indicator (compass)
Manifold pressure gauge (for each altitude engine/turbo/supercharged)Safety belt
Signaling device and flotation gear (when for hire beyond power-off gliding distance of the shore)
(2 is for all the previous letters twice)
Fuel gauge (quantity for each tank)Landing gear position indicator (for retractable landing gear)
Emergency locator transmitter
Anti-collision light system
(any additional equipment required by the Pilots Operating Handbook)
Additionally required for VFR night 91.205(c)
FLAPS (additional equipment required for night flight)
Fuses (3 spare for each type)
Landing light (if for hire)
Anti-collision lights
Position lights
Source of electrical power (adequate for all installed electrical and radio equipment)
IFR Equipment Required
91.205 (d) Additionally required for IFR flight(in addition to those required by VFR night)
GRABCARD
Generator/Alternator
Radios (appropriate for flight)
Altimeter (sensitive/adjustable)
Ball
Clock (second hand sweep or digital)
Attitude indicator
Rate of turn
Directional gyro
Risk Elements
(Pilot in command, aircraft, environment, operation)
PAVE your way over the risks
Pilot
Aircraft
enVironment
External pressures
Decide Model
Elements of the DECIDE model for decision making
Detect a change needing attention
Estimate the need to counter or react to change
Choose the most desirable outcome for the flight
Identify actions to successfully control the change
Do something to adapt to the change
Evaluate the effect of the action countering the change
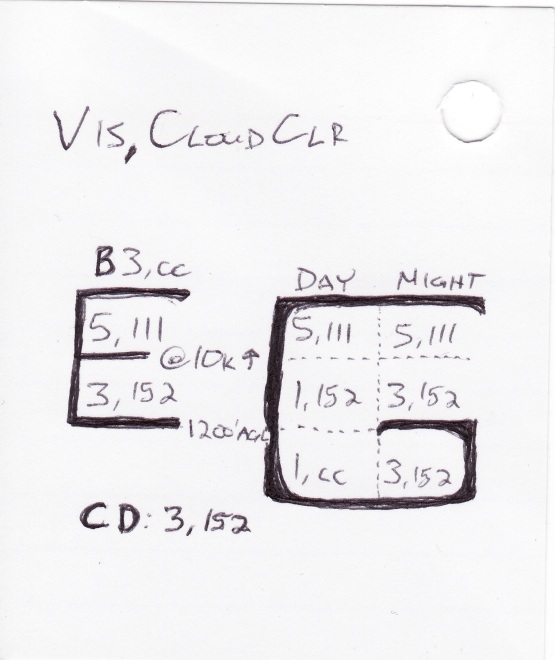
Visibility/Cloud Clearance Requirements
Special VFR requires
- ATC clearance
- Clear of Clouds
- 1sm visibility (at least)
- Daytime (sunrise to sunset)
Special Use Airspace
(United States)
PRWAMCN: Public Relations over a [crash] WAM CNn covers it
Prohibited
Restricted
Warning areas
Alert areas
Military Operations Areas
Controlled Firing Areas
National Security Areas
LOST 5 C’s
Confess
Climb
Conserve
Communicate
Comply
VFR Cross Country
East is Least, West is Best
VFR Cruising Altitudes 91.159
Based upon Magnetic Course (MC=True Course subtract Variation)
0° to 179° = Odd thousand +500 feet
180° to 359° = Even thousand +500 feet
Also for computing groundspeed winds Winds from the left you subtract to heading Winds from the right you add to heading
Night
Logging: FAR 1.1: civil twilight sunrise/sunset (generally when artificial illumination is required to read outside…on the ground)
Recency (to carry passengers at night) 61.57(b): 1 hour after sunset, 1 hour before sunrise (for both carrying passengers and accomplishing night recency requirements)
Position lights required: 91.209 Sunset to Sunrise
Hazardous Attitudes
Five hazardous attitudes and antidotes
I’M AIR (like I’m err or I’m erring)
Invulnerability–It could happen to me
Macho–Taking chances is foolish
Antiauthority–Follow the rules, they are usually right
Impulsivity–Think first—not so fast
Resignation–I can make a difference, I am not helpless
Multi-Engine Aerodynamics
Identifying the critical engine: (It is critical to remember the past)
PAST
P-factor
Accelerated slipstream
Spiraling slipstream
Torque Vmc certification requirements 23.149
SMACFUM The conditions for how Vmc is determined for an aircraft.
Standard day at sea level
Max power
Aft CG
Critical engine windmilling
Flaps/gear downUp to 5° bank
Most unfavorable weight
Lost engine memorized checklist
Maintain directional control
Blue line or better (82KIAS DA42)
Max power on the operating engine
Flaps up
Gear up
Identify: dead foot dead engine
Verify: throttle position, instruments, proceed to feather/shut down
Fundamentals of Instruction
Characteristics of Learning
Purposeful—unique with individual’s past experience
Result of Experience—must experience to learn
Multifaceted—verbal, conceptual, emotional
Active Process—to learn: react and respond
Laws of Learning
Readiness—reason to learn–motivation
Exercise—most often repeated is best remembered
Effect—best with pleasant feeling
Primacy—teach right the first time
Intensity—vivid, dramatic, or exciting
Recency—most recent is best remembered
Levels of Learning
Rote–memorization
Understanding—perceiving and learning
Application—achieving skill to apply and perform
Correlation—associating learning to previously learned
Domains of Learning
Cognitive—recall information, understanding, analysis, application.
Affective—awareness, integration, emotion toward the experience
Psychomotor—observation, habit, physical skill, coordination of muscles
Memorize Endorsements
Types of flight instructor endorsements
Park Off Pigs
Pilot certificates
Aircraft rating
Recency of experience requirement
Knowledge test
Operating privilege
Flight instructor certificate
Flight review
Practical test
Instrument rating
Ground instructor certificate
Student pilot certificate
I’M SAFE
Illness – Is the pilot suffering from any illness or symptom of an illness which might affect them in flight,
Medication – Is the pilot currently taking any drugs (prescription or over-the-counter),
Stress – Psychological or emotional factors which might affect the pilot’s performance,
Alcohol – consider their alcohol consumption within the last 8 to 24 hours (.04 limit),
Fatigue – Has the pilot had sufficient sleep and rest in the recent past, and
Eating – Is the pilot sufficiently nourished?
Great article.
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve discovered It positively useful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to give a contribution & aid other users like its helped me. Great job.
Thank you for your donation!
Love this! It was very helpful to brush up on. Thanks!
Great Job!!!!! I would only add when the aircraft registration is nullified.
30FTDUC “30 Foot Duck”
30 – Thirty Days After Death
F – Foreign Registry (change to another country for aircraft registration)
T – Transfer of Ownership (If you sell your airplane)
D – Destroyed (If the aircraft is destroyed)
U – United States citizenship revoked
C – Cancelled
That’s Awesome, thanks for that!
Helped a lot! Collected in one place n organized!
What does the acronyms the three p s mean
Perceive
Process
Perform
Good site! I truly love how it is simple on my eyes and the data are well written. I am wondering how I might be notified when a new post has been made. I’ve subscribed to your RSS which must do the trick! Have a nice day!
Everything is very open with a very clear clarification of the
challenges. It was definitely informative.
Your site is very useful. Thanks for sharing!
Brilliant! I have the memory of a goldfish so this has helped me immensly.
Question:
is it favorable to retract the flaps first and than the landing gear or the other way around in the Lost engine memorized checklist?
In my opinion it is better to retract the landing gear since it is not supporting lift at all and as a second step the flaps
please respond – It’s a long time since I aired my wings…
It may just depend on your airplane. For a single-engine plane, the gear isn’t helping you until you need to land. For a multi-engine airplane, the stability and decreased Vmc you get from the gear is more favorable than the drag it produces. Lots of variables to consider.